QR codes are everywhere! From restaurant menus to museum exhibits, these ubiquitous squares have become an integral part of our daily lives. But have you ever stopped to wonder about the technology behind them? This guide will demystify QR codes, providing a simple, straightforward explanation of how they work and, most importantly, a clear guide on how to scan QR codes with your phone. Learn how to unlock the information hidden within these digital patterns and access everything from website links to exclusive content effortlessly.
This article will cover the basics of scanning QR codes using the built-in capabilities of your smartphone. Whether you have an Android or an iPhone, we’ll walk you through the simple steps needed to quickly and effectively scan a QR code. You’ll learn how to access the QR code scanner feature and what to do if you encounter any issues. Unlock the secrets of QR codes today and experience the convenience and accessibility they offer.
Understanding QR Codes and Their Uses
QR codes, short for Quick Response codes, are two-dimensional barcodes that can store a variety of information. Unlike traditional barcodes that hold limited data, QR codes can contain significantly more, including website URLs, contact information, product details, and even Wi-Fi network credentials. Their design, a square matrix of black and white modules, allows for rapid decoding, hence the name “Quick Response.”
These codes bridge the physical and digital worlds, providing a convenient way to access online information from physical objects. Simply scanning a QR code with your smartphone’s camera can instantly connect you to a website, download an app, or display product information. This ease of use has led to their widespread adoption across various industries.
Common uses of QR codes include:
- Marketing and Advertising: Providing quick access to promotional offers, website links, or product demos.
- Payments and Transactions: Facilitating contactless payments and mobile banking.
- Product Information: Displaying details about ingredients, manufacturing processes, or user manuals.
- Event Ticketing and Registration: Streamlining event check-in processes.
Built-in QR Code Scanners on Smartphones
Most modern smartphones come equipped with built-in QR code scanners, eliminating the need for separate apps. These integrated scanners are often seamlessly incorporated into the camera app or other system utilities.
Accessing the built-in scanner often involves simply opening your phone’s camera app and pointing it at the QR code. The phone should automatically recognize and process the code. Some devices may require enabling the QR code scanning feature within the camera settings.
On iOS devices (iPhones and iPads), the camera app natively supports QR code scanning. No additional setup is typically required. Just open the camera and point it at the code.
Android devices often have integrated QR code scanning functionality within the camera app as well. However, the specific method may vary depending on the manufacturer and Android version. Some Android phones may have a dedicated QR code scanner within the Google Assistant or Google Lens app.
Using Third-Party QR Code Scanner Apps
While most modern smartphones have integrated QR code scanners, some users may prefer the added features and functionality of third-party apps. These apps often provide benefits such as faster scanning speeds, batch scanning capabilities, generating QR codes, and history logging.
Numerous QR code scanner apps are available on both the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. When choosing an app, consider factors like user reviews, security features, and any additional functionalities that align with your needs. After installing the app, simply launch it and follow the on-screen instructions, which typically involve pointing your phone’s camera at the QR code.
Some popular third-party QR code scanner apps include:
- QR Code Reader
- Kaspersky QR Scanner
- NeoReader QR & Barcode Scanner
Remember to carefully review the permissions requested by any third-party app before installation. Prioritize apps from reputable developers to minimize security risks.
Troubleshooting QR Code Scanning Issues
Occasionally, you might encounter problems when trying to scan a QR code. Here are some common issues and how to resolve them:
Poor Lighting or Glare
Lighting plays a crucial role in QR code scanning. Ensure the code is adequately lit and avoid glare, which can interfere with the camera’s ability to capture the pattern.
Distance and Focus
Hold your phone at a reasonable distance from the QR code. Too close or too far can prevent a successful scan. Ensure your camera is properly focused.
Damaged or Obscured QR Codes
A damaged or partially covered QR code may be unreadable. If the code is scratched, faded, or obstructed, try to find a cleaner or undamaged version.
Camera Permissions
Verify that the QR code scanner app has permission to access your camera. Check your phone’s settings and enable camera access for the app if it’s disabled.
Tips for Scanning QR Codes Effectively

Scanning QR codes is usually straightforward, but a few tips can ensure a smooth and successful experience. Hold your phone steady to allow the scanner enough time to focus and interpret the code. Avoid shaky hands and sudden movements. Ensure the entire QR code is visible within the scanner’s frame. Partial codes won’t scan properly.
Lighting conditions play a crucial role. While most modern scanners can handle dimly lit environments, extremely low light or glare can hinder the process. Adjust your position or use a flashlight if needed. If the code is printed on a reflective surface, try tilting your phone to minimize glare.
Clean the camera lens on your phone. Dust, smudges, or fingerprints can obstruct the scanner’s view and prevent accurate decoding. A quick wipe with a soft cloth can often resolve scanning issues. Finally, maintain a reasonable distance from the QR code. Too close, and the scanner may struggle to focus; too far, and the code may appear too small.
Ensuring Security When Scanning QR Codes
While QR codes offer convenience, it’s crucial to prioritize security when scanning them. Malicious QR codes can redirect you to harmful websites or download malware onto your device. Therefore, exercise caution and follow these safety guidelines.
Inspect the QR Code: Before scanning, visually examine the QR code for any signs of tampering or damage. If it looks suspicious, avoid scanning it.
Verify the Source: If the QR code is linked to a promotion or offer, confirm the legitimacy of the source. Check their official website or social media channels to ensure the promotion is genuine.
Preview the URL: Most QR code scanners display a preview of the URL before opening it. Carefully examine the URL. Look for misspellings, unusual characters, or shortened URLs that could mask a malicious destination. Avoid clicking on suspicious links.
Use a Reputable QR Code Scanner: Choose a well-regarded QR code scanning app from a trusted source, such as the official app store for your device. Avoid using unknown or unofficial scanners.
Keep Your Software Updated: Ensure your operating system and security software are up-to-date to protect against the latest threats.
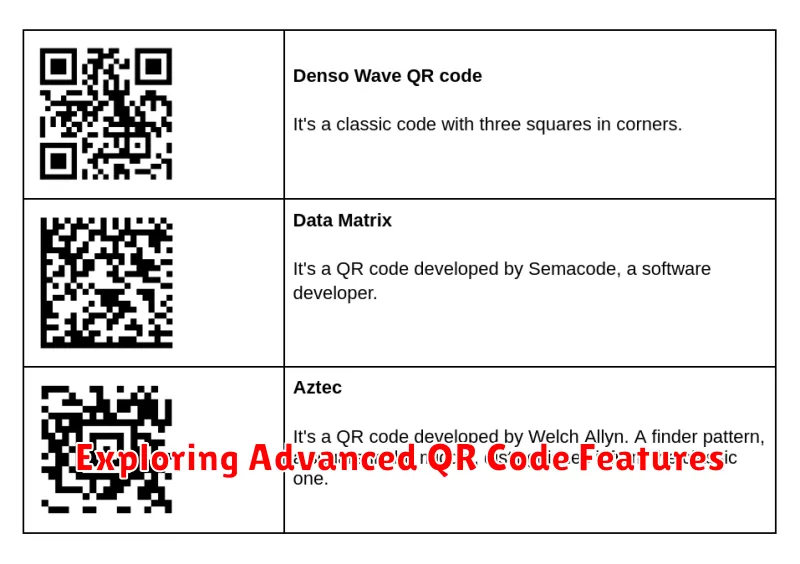
Exploring Advanced QR Code Features
Beyond basic website links, QR codes can hold a wealth of information and offer enhanced functionality. Dynamic QR codes, for example, allow content modification after creation, providing flexibility for marketing campaigns or updating information. This contrasts with static QR codes, where the embedded information is permanent.
QR codes can also store contact information (vCard) enabling users to quickly add someone to their address book. They can generate calendar events pre-filled with date, time, and location, streamlining scheduling. Furthermore, QR codes can configure Wi-Fi access, eliminating the need to manually enter network credentials.
Some advanced QR codes offer features like geo-location, which can be used for check-ins or location-based services. They can also initiate phone calls or send pre-written SMS messages.

